Secure Digital (SD) is a nonvolatile memory card used extensively in portable devices, such as mobile phones, digital cameras, GPS navigation devices, handheld consoles, and tablet computers.
The Secure Digital standard was introduced in August 1999 as an evolutionary improvement over MultiMediaCards (MMC). The Secure Digital standard is maintained by the SD Association (SDA). SD technologies have been implemented in more than 400 brands across dozens of product categories and more than 8,000 models
SD
The first-generation Secure Digital (SDSC or Secure Digital Standard Capacity) card was developed to improve on the MultiMediaCard (MMC) standard, which continued to evolve, but in a different direction. The SD cards changed the MMC design in several ways:- Asymmetrical slots in the sides of the SD card prevent inserting it upside down, while an MMC goes in most of the way but makes no contact if inverted.
- Most SD cards are 2.1 mm (0.083 inches) thick, compared to 1.4 mm (0.055 inches) for MMCs. The SD specification defines a card called Thin SD with a thickness of 1.4 mm, but they are rare, as the SDA went on to define even smaller form factors.
- The card's electrical contacts are recessed beneath the surface of the card, protecting them from contact with a user's fingers.
- The SD specification envisioned capacities and transfer rates exceeding those of MMC, and these have both grown over time. For a comparison table.
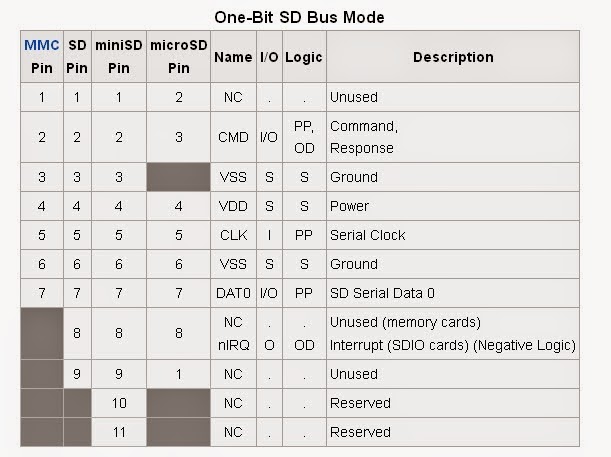
 Micro sd card pins are:
Micro sd card pins are:- CS-Card Select
- DI-Data In [MOSI]-Master, Out Slave Input
- VSS-Ground
- VDD-Power
- CLK-Clock [SCLK]-Serial Clock
- DO-Data Out [MISO]-Master Input, Slave Output
- NC (Memory Cards)